The coronavirus pandemic severely disrupted Chinese businesses during the first few months of the year, as demonstrated by a 6.8% decline in China’s GDP for Q1 2020.
China also recorded declines in industrial output (-8.4%), retail sales (-19.0%), foreign trade (-6.4%) and foreign direct investment (-10.8%) in Q1 2020.1 However, as many Chinese businesses, factories and people return to work, economic indicators and financial markets are beginning to show signs of recovery.
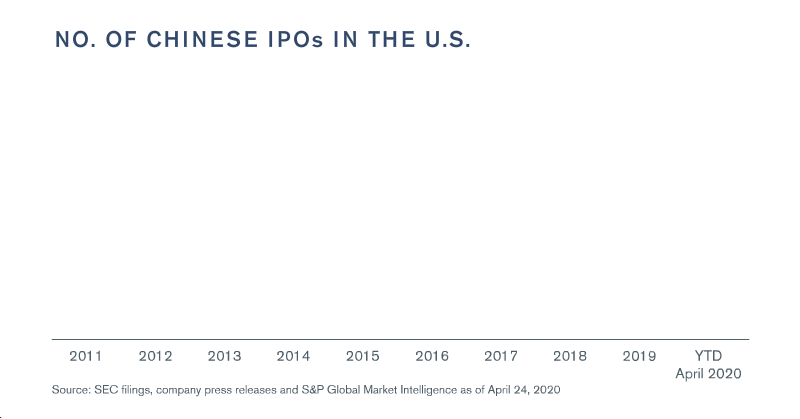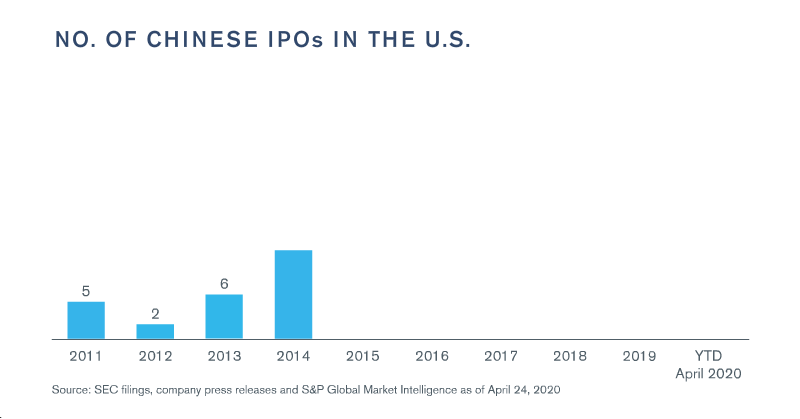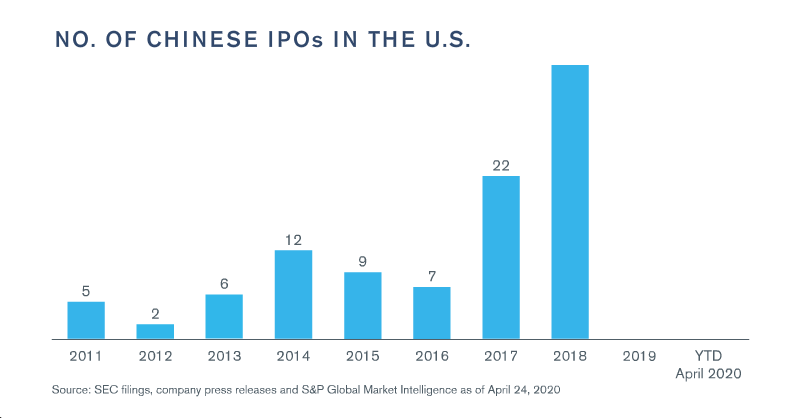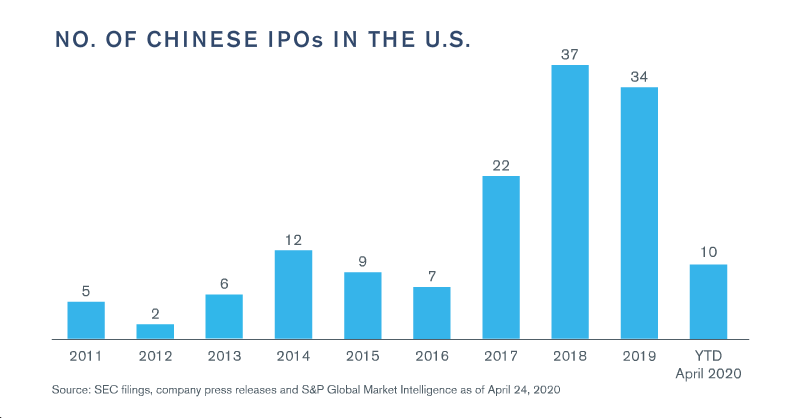
Capital markets activity for Chinese companies also felt the impact of COVID-19, as market volatility and uncertainty slowed the pace of both U.S. and Hong Kong IPOs of Chinese companies through the first four months of the year.2
Going-private transaction activity for U.S.-listed companies based in China remains below the peak level seen in 2016. However, 2020 has the potential for a substantial uptick in deal value, as companies with pending going-private proposals represented approximately USD 13 billion in total market capitalization as of May 7, 2020.2
Sources
1 China National Bureau of Statistics and China Ministry of Commerce
2 SEC filings, company press releases and S&P Global Market Intelligence as of May 7, 2020
Connect With Us
Stay Ahead with Kroll
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Advisory
Kroll’s top ranked M&A Advisory practice spans sell-side, buy-side, due diligence, deal strategy and structuring, and capital raising.
Transaction Opinions
Our Transaction Opinions solutions span fairness opinions, solvency opinions, ESOP/ERISA advisory, board and special committee advisory, and complex valuations.
Distressed M&A and Special Situations
Kroll professionals have advised hundreds of companies, investors and other stakeholders at all stages of distressed transactions and special situations.
Transaction Advisory Services
Kroll’s Transaction Advisory Services platform offers corporate and financial investors with deep accounting and technical expertise, commercial knowledge, industry insight and seamless analytical services throughout the deal continuum.
Debt Advisory
Kroll has extensive experience raising capital for middle-market companies to support a wide range of transactions.